tl;dr
This is a simple stack based VM
25-27 opcodes and 8 different constraints
Extract the constraints
Use z3 to find a satisfying model
Challenge Points : 245Challenge Solves : 20Challenge author : EvilMuffinHa Solved by : AmunRha , Freakston , barlabhi
Description Introduction This is a simple VM which has around 25-27 opcodes with instructions simple enough to be emulated. This is a stack based VM.
The VM implements several constraints on the input bytes which can be solved using z3 SMT solver.
The VM implemented a puzzle called kenken
Solution I chose python to write the disassembler in with several helper functions, at first I tried extracting the constrains one by one, which eventually worked, but then I was able to write a automatic extractor for the disassembly.
There were two files, one the binary and the data file in which the list of instructions contain.
This when fed to the z3 solution script will get us the required input.
Most of the operations take their operands from the stack, so there wasn’t much complexity in terms of implementation.
p.s. This will be a short write up
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 def disasm (op, c) : if c > dump_len: return -1 extract(op,rsp,ctr1) dctr = ctr1 + 1 if op == 0x1 : rsp.append(rsp[-1 ]) ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x2 : rsp = rsp[:-1 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x3 : if rsp[-1 ] == -1 : rsp = rsp[:-1 ] ctr1+=1 elif rsp[-1 ] != 0 : print(f"[+] RETURN: {rsp[-1 ]} " ) return -1 else : print("[+] READING FLAG FILE" ) return 1 elif op == 0x10 : rsp[-2 ] = rsp[-1 ] + rsp[-2 ] rsp = rsp[:-1 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x11 : rsp[-2 ] = rsp[-1 ] - rsp[-2 ] rsp = rsp[:-1 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x12 : rsp[-2 ] = rsp[-1 ] * rsp[-2 ] rsp = rsp[:-1 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x13 : rsp[-2 ] = rsp[-1 ] // rsp[-2 ] rsp = rsp[:-1 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x14 : rsp[-2 ] = rsp[-1 ] % rsp[-2 ] rsp = rsp[:-1 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x15 : tmp = rsp[-1 ] rsp.pop(-1 ) res = rsp[-2 ]*rsp[-1 ]%tmp rsp = rsp[:-2 ] rsp.append(res) ctr1 = dctr elif op == 0x16 : rsp[-2 ] = 1 if rsp[-1 ] == rsp[-2 ] else 0 ctr1+=1 rsp = rsp[:-1 ] elif op == 0x17 : if rsp[-1 ] < 0 : rsp[-1 ] = -1 elif rsp[-1 ] > 0 : rsp[-1 ] = 1 ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x20 : rsp.append(inp[ii]) ii+=1 ctr1 = dctr elif op == 0x21 : v30 = rsp[-1 ] rsp = rsp[:-1 ] ctr1 = dctr print(chr(v30)) output.append(v30) elif op == 0x22 : ctr1+=3 rsp.append((f[dctr+1 ]<<8 ) | f[dctr]) elif op == 0x30 : v30 = rsp.pop(-1 ) ctr1 = abs(v30) elif op == 0x31 : if rsp[-2 ] != 0 : rsp = rsp[:-2 ] ctr1+=1 else : ctr1 = rsp[-1 ] rsp = rsp[:-2 ] elif op == 0x32 : if rsp[-2 ] != 0 : ctr1 = rsp[-1 ] rsp = rsp[:-2 ] else : rsp = rsp[:-2 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x33 : if rsp[-2 ] < 0 : ctr1 = rsp[-1 ] rsp = rsp[:-2 ] else : rsp = rsp[:-2 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x34 : if rsp[-2 ] <= 0 : rsp = rsp[:-2 ] ctr1+=1 else : ctr1 = rsp[-1 ] rsp = rsp[-2 ] elif op == 0x35 : if rsp[-2 ] > 0 : rsp = rsp[:-2 ] ctr1+=1 else : ctr1 = rsp[-1 ] rsp = rsp[-2 ] elif op == 0x36 : if rsp[-2 ] >= 0 : ctr1 = rsp[-1 ] rsp = rsp[:-2 ] else : rsp = rsp[:-2 ] ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x40 : v33 = rsp.pop(-1 ) data[v13] = v33 ctr1 = dctr elif op == 0x41 : ctr1+=1 rsp.append(data[v13]) elif op == 0x50 : v13+=1 ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x51 : v13-=1 ctr1+=1 elif op == 0x52 : v13 = (rsp[-1 ]+v13) & 0xff ctr1+=1 rsp = rsp[:-1 ] elif op == 0x53 : v13 = (v13 - rsp[-1 ]) & 0xff ctr1+=1 rsp = rsp[:-1 ] else : print(f"""[!] UNKNOWN OPCODE: {hex(op)} """ , end='' ) return -1 return ctr1
Commenting the lines specified can get us the extracted constrains.
I wrote a small parser on my disassembly which will get the proper constraints.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 equations = {"add_2" :[], "add_3" :[], "equate_3" : [], "equate_4" :[], "mod_equate_2" :[], "sub_2" :[], "equal_2" :[]} def parse (bbl, f) : PUSH_OPERAND = [0x22 , 0x52 , 0x41 ] SUB_2 = (16 ,2 ) EQUATE_3 = (21 ,3 ) EQUATE_4 = (28 ,4 ) ADD_2 = (13 ,2 ) ADD_3 = (19 ,3 ) MOD_EQUATE_2 = (64 ,2 ) EQUAL_2 = (7 ,2 ) for llist in bbl: eq = [] bbl_len = len(llist) i = 1 while True : if i+2 >= bbl_len: break if [llist[i][0 ],llist[i+1 ][0 ],llist[i+2 ][0 ]] == PUSH_OPERAND: ctr = llist[i][1 ] res = f[ctr+1 ] eq.append(res) i+=3 i+=1 ctr = llist[0 ][1 ] res = [f[ctr+1 ]] if bbl_len == SUB_2[0 ]: eq = eq[:SUB_2[1 ]] + res equations["sub_2" ].append(eq) elif bbl_len == EQUATE_3[0 ]: eq = eq[:EQUATE_3[1 ]] + res equations["equate_3" ].append(eq) elif bbl_len == EQUATE_4[0 ]: eq = eq[:EQUATE_4[1 ]] + res equations["equate_4" ].append(eq) elif bbl_len == ADD_2[0 ]: eq = eq[:ADD_2[1 ]] + res equations["add_2" ].append(eq) elif bbl_len == ADD_3[0 ]: eq = eq[:ADD_3[1 ]] + res equations["add_3" ].append(eq) elif bbl_len == MOD_EQUATE_2[0 ]: eq = eq[:MOD_EQUATE_2[1 ]] + res equations["mod_equate_2" ].append(eq) elif bbl_len == EQUAL_2[0 ]: eq = eq[:EQUAL_2[1 ]] + res equations["equal_2" ].append(eq) return equations
There were in total 8 different constraints applied on the input bytes, which was added to z3.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 def set_idx (set_to) : for i in set_to: s.add(f[i[0 ]] == i[1 ]) def sub2 (s_list) : for i in s_list: s.add(f[i[1 ]] - f[i[0 ]] == i[2 ]) def add2 (a2_list) : for i in a2_list: s.add(f[i[0 ]]+f[i[1 ]] == i[2 ]) def add3 (a3_list) : for i in a3_list: s.add(f[i[0 ]]+f[i[1 ]]+f[i[2 ]] == i[3 ]) def equate3 (e3_list) : for i in e3_list: res = (f[i[2 ]]*f[i[1 ]])%0x7fff s.add((f[i[0 ]]*res)%0x7fff == i[3 ]) def equate4 (e4_list) : for i in e4_list: res = (f[i[3 ]]*f[i[2 ]])%0x7fff res = (f[i[1 ]]*res)%0x7fff s.add((f[i[0 ]]*res)%0x7fff == i[4 ]) def mod_equate2 (m2_list) : for i in m2_list: s.add((f[i[1 ]] % f[i[0 ]]) * (f[i[0 ]] % f[i[1 ]]) == 0 ) s.add(f[i[0 ]] != f[i[1 ]]) s.add(UDiv((UDiv(f[i[1 ]], f[i[0 ]]) + UDiv(f[i[0 ]], f[i[1 ]])),1 ) == i[2 ]) def distinct_add () : for i in off: s.add(f[i[0 ]] != f[i[1 ]])
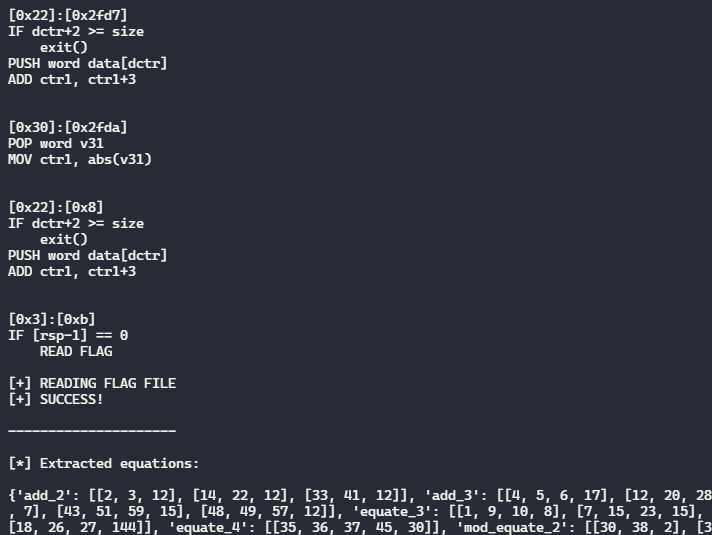
Running the script gives us the disassembly, and the extracted constraints
and pasting the extracted constraints to z3, gives us the input to be given,
pB738150rHt60714NP501s92420G3xUY013;Wo{=69h42Ob736B1y{@?1047uw`6
Sending this over the given nc connection, gives us the flag,
Flag: flag{kenken_is_just_z3_064c4}
Links to required files,2k_disassembler.py helper.py z3_solver.py